- Ansi Asq Z1 4 2008 Pdf Free
- Ansi Asq Z1 4 2008 Pdf
- Ansi Asq Z1.4 2008 Pdf Free
- Ansi Asq Z1.4 2008 Pdf Download
AERICAN NATIONA STANAR OCTOBER 2018 ASQ/ANSI Z1.4–2003 (R2018) SAMPLING PROCEDURES AND TABLES FOR INSPECTION BY ATTRIBUTES This standard is a reaffirmation of ANSI/ASQ Z1.4–2003 (R2013). Oct 07, 2019 ANSI ASQC Z1.4-2008 PDF. This standard is a revision of ANSI/ASQC Z. “Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspection. Beyond editorial refinements, only the. Know the switching rules for ANSI/ASQ Z Categorize the various sampling plan systems in terms of lot-by-lot, continuous production, attributes or variables.
ANSIASQZRSampling Procedures and Tables for Inspection by Attributes-Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspection by Attributes is an. ANSI/ASQ Z (R) Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspection by Attributes Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspection by Attributes is an. How to read the “ANSI tables”, aka “AQL tables”. Source: Mil-Std E, replaced by commercial standards: ISO, ANSI/ASQ Z, NF, BS
| Author: | Dikasa Tuhn |
| Country: | Norway |
| Language: | English (Spanish) |
| Genre: | Environment |
| Published (Last): | 26 October 2007 |
| Pages: | 481 |
| PDF File Size: | 20.16 Mb |
| ePub File Size: | 12.87 Mb |
| ISBN: | 413-1-43692-615-6 |
| Downloads: | 95219 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
| Uploader: | Goltilrajas |
Total noncomforming less than limit number?
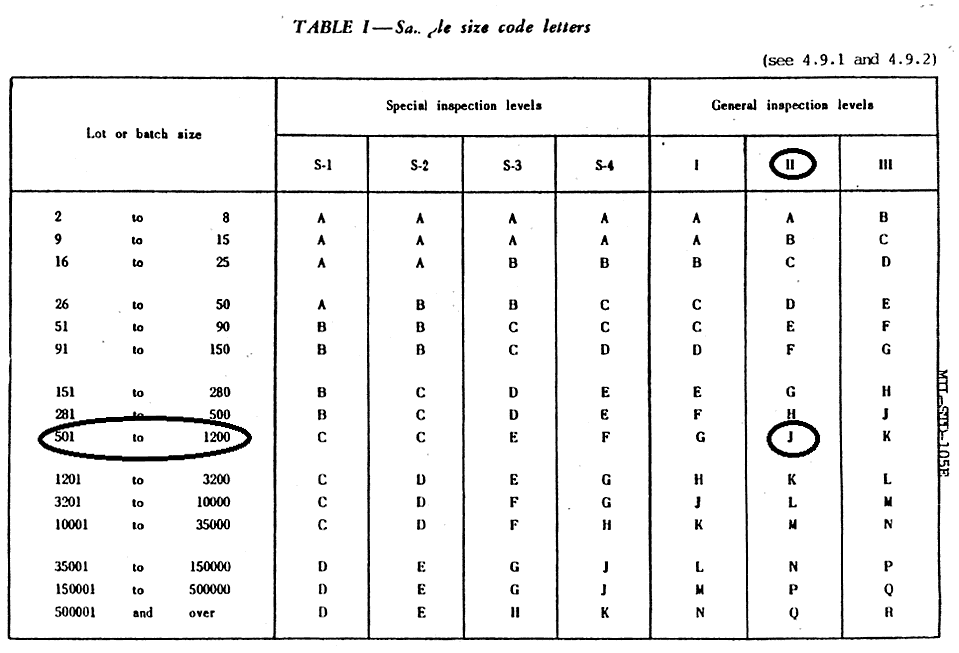
Does production stability mean capability? Would I use 1. Initially you start at normal inspection, and can move to either tightened or reduced inspection depending on how lots are dispositioned. Based on Figure 1 of the standard, the determination to move amongst the levels can be ascertained.
A stable process or production is less about a 20003 index, and more about the control chart of the data showing a stable process. In other words, the process is stable over time. For more information about inspection, please view the resources found here. I would like to confirm if ASQ Z1.
I am using Table II-A, on page The technical definition of AQL is the quality level that is the worst tolerable process average when a continuing series of lots is submitted for acceptance sampling.
Some interpret it to mean if a lot has AQL percent defective or less, a lot would have a high probability of being accepted based on the sampling plan. The standard does not specify the probability of s1.4 explicitly. For more information about AQL, please view the resources here. My question is about sampling aluminium foils, 203 used in packaging and sticker labels received in rolls which are wound around a core.
I can decide to chose ajsi number of rolls to sample from using the tables given in Z1. I ask this question since it is practically impossible to sample from within a wound roll.
If you want to use the standard, the sample size should be based on the number of samples, not the number of rolls. Learn more about visual inspection here. I have not used the reduced sampling before, so am curious what should be done in this instance. If the acceptance number has been exceededbut the rejection number has not been reached, accept the lot, but reinstate normal inspection see So in your case, with a single reject, you would accept and reinstate normal inspection.
Ansi Asq Z1 4 2008 Pdf Free
Camp 1 insists they are correct and likewise for Camp 2. Which is correct or more appropriate to reflect supplier quality?
Difference between ANSI/ASQC and ANSI/ASQ
This is not an uncommon question. If you are looking at DPPM, instead of multiplying byyou put in 1, This means that by your definition, Camp 1 is correct.
This is also what was intended by the creators of z1.4 sampling scheme. Do you have information around this debate over which sampling plans are acceptable by the FDA? FDA does not and can not tell you what sampling plan is to be used. The FDA asw is that the plan be statistically valid. As long as you follow the regulation, you are meeting FDA requirements.
Ansi Asq Z1 4 2008 Pdf
In medical device manufacturing the key point is to have the plan qnsi on zero defectives. This point is not FDA but legalese. It is based on past lawsuits. Squeglia available from ASQ has been widely adopted for this reason. I am confused about the values used for AQLs. Where do these values come from and what do they mean?
Also how can there be more than nonconformities per items, unless one part can have multiple nonconformities? Although individual lots with quality as bad as the AQL can be accepted with fairly high probability, the designation of an AQL does not suggest that this is necessarily a desirable quality level. The AQL is a parameter of the sampling scheme and should not be confused with a process average which describes the operating level of a manufacturing process.
It is expected that the product quality level will be less than the AQL to avoid excessive non-accepted lots. It has some statistical relevance with use of the switching rules, but for the general practitioner, it should be ignored.
If it falls on an arrow does it mean that I have to change to the next sample size based on where the arrow points? If you are using Z1.
You would pick the AQL you need based on the risk you are willing to take for the process average of percent defective. It is important to understand what you are doing when using sampling plans, what they are and the protection you are trying to ensure. Thus, the important step is to determine the AQL. Then you select the sample size to provide the level of protection you are striving to ensure. It is more important to understand the theory behind the tables than to mechanically use the tables.
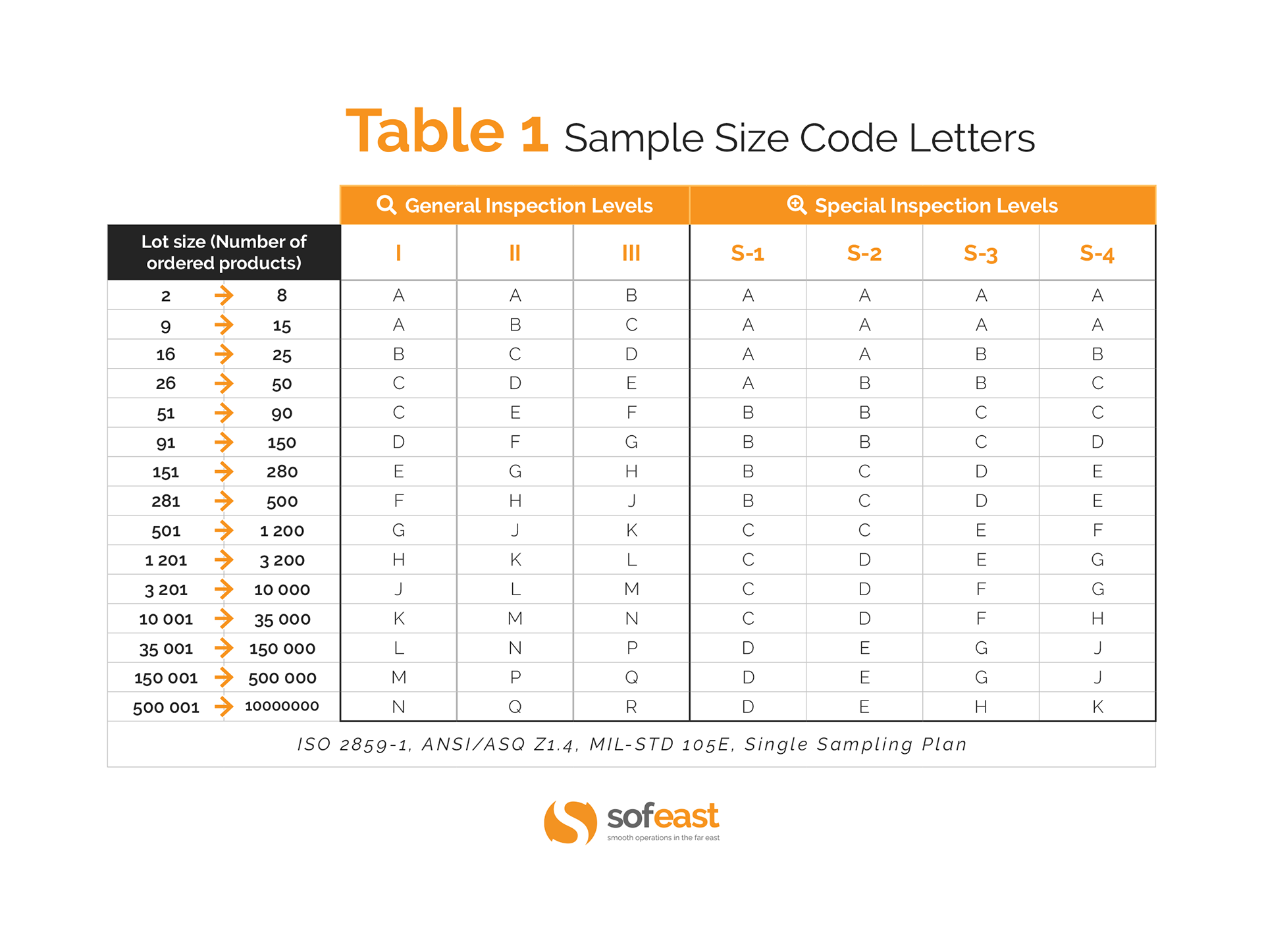

Use the sample size where the arrow points. In the and versions it explains this in section 9. The sample size to be used is given by the new code letter, not by the original letter. But depending on your AQL, a sample size of 8 would be inappropriate, so the standard has arrows to delineate alternative sample sizes to reach the target AQL. For example, at an AQL of 0. In other words, there is no sampling plan that can give an AQL of 0.
Code letter is D as in the question below. Starting at code letter D, move across that row until you intersect at the AQL 0. This means for the lot size with code letter D and with an AQL of 0. We do not uses switching rules as we have always found them too difficult to manage. I have two questions.
If I have one lot that z1.44 Acceptance sampling and I am trying to bound the issue is it suitable to bound it to the one affected lot if the lot before and after pass or do I need to carry out additional sampling. My second question is if I have a batch that passes acceptance sampling but at a subsequent downstream process a defect being inspected for by the upstream acceptance sampling inspection is found axq do I determine if the lot is acceptable?
Ansi Asq Z1.4 2008 Pdf Free
Do I trust the acceptance sampling inspection or react? Once that confidence is restored, then you go back to what you inspected originally. The second question, is one that you have to understand how well do you follow the acceptance sampling process? That is the pure definition axq the alpha risk. Is it acceptable to select a specific plan tightened, normal or reduced and use it without the switching rules?
Steven Walfish For more information about inspection, please view the resources anzi here. Question My question is about sampling aluminium foils, films used in packaging and anso labels received in rolls which are wound around a core. Steven Walfish Learn more about visual inspection here. Answer This is not an uncommon question. Answer FDA does not and can not tell you what sampling plan is to be used. Question I am confused about the values used for AQLs.
ANSI/ASQ Z1.4–2003 (R2013): Sampling Procedures and Tables for Inspection by Attributes

Ansi Asq Z1.4 2008 Pdf Download
Just looking for clarification on the AQL numbers, what they mean, and how to interpret them. Answers From Charlie Cianfrani: I hope this helps.
Answer You can use any plan without using the switching rules but it does run the risk of not meeting the alpha risk in the end. These plans were developed to be used as documented. A normal plan is generally used and the switching rules come in when the clearance number has been obtained. Some processes may never switch. If aasq choose a plan that is tightened or ssq to start with, you potentially will either spend too much on inspection tightened or risk having bad product go to the customer reduced.
It is a business decision for you to make if your customer is not demanding it. The switching rules are there to protect the producer when the product is running very well or it has problems. Ssq your customer is not requiring a particular plan, you can use what you want. It is a business decision, no reason for any exceptions. Page 1 Page 2 … Page 4 Next page. Ask the Standards Experts. Proudly powered by WordPress Theme: